ELECTRICAL EQUATIONS
Voltage =
Volts Current = Amps Resistance = Ohms
Voltage =
Current x Resistance
Current =
Voltage / Resistance
Resistance =
Voltage / Current
Watts =
Joules/second
Volts * Amps
= Watts
Electric
Power = rate @ which energy is transformed from one form to another
Power =
Watts
1 Kilowatt is
1,000 watts
- 1 watt is equal to 0.001 kilowatt.
Watts * Time
= Joules or total energy consumed
Increasing
Voltage increase the current
Increasing
the Resistance will decrease the current
Voltage
& current are directly proportional
Current
& Resistance are inversely proportional
HOW STATIC ELECTRICITY IS PRODUCED
1. When two different
objects that are insulators (such as a plastic rod and silk cloth) are rubbed
together, electrons move from one object to another.
2. One object becomes
negatively-charged, and the other object becomes positively-charged.
3. The more rubbing, the
more electrons are transferred, and the larger is the charge built up.
4. Unlike charges
(positive and negative) attract each other.
· Current Electricity
or electric current is the movement of negatively-charged electrons through
wires or objects with metals, carbon or water.
· Conductors are
substances that allow electrons to travel easily through them (e.g. metals,
carbon and water).
· Insulators or
non-conductors are substances that do not allow electrons to travel easily
through them (e.g. plastic and wood).
· Resistors are
substances that are poor conductors. They convert much of the energy of moving
electrons into light, heat or sound energy in light bulbs and stereos.
·
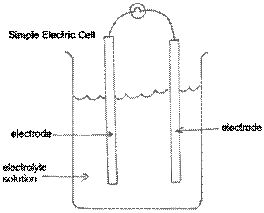
A simple cell
consists of 2 different conductors (electrodes) partly covered by an
acidic or ionic solution (electrolyte solution).
· Different combinations of electrodes produce different
· voltages.
· For example,
electrodes of zinc
and copper produce 1.1 volts, whereas electrodes of
aluminum
and carbon produce
2.4 volts.
· Rechargeable Cells
(e.g. lead-acid cells) are cells that can be recharged when they go 'flat' by
reversing the chemical reaction.
· Electrical power is
the amount of electrical energy used
by an appliance every
second. It is measured in Watts.
· When paying for
electricity, we use the unit kiloWatt-hour (kWh). One kWh is the energy used by
a 1000 watt appliance switched on for one hour.
· Example:
Q. A 200 watt TV set is
used for 6 hours. How many kilowatt-hours of electricity were used?
A.
Number of kWh
|
= kilowatts × number of rating hours
|
= (200 W⁄1000)
× 6 h
|
= 1.2 kWh
|
SERIES CIRCUIT
- Series Circuit - a circuit where
the components are connected one after the other into a 'circle'.
- Ammeter - This device is used to
measure current in amperes (A). It must be wired into the circuit
in series.
- Disadvantages of Series Circuits -
As more light bulbs are connected in series, the brightness of all bulbs
decreases.
PARALLEL CIRCUITS
- Parallel Circuits are combined
circuits where components such as light bulbs glow equally brightly.
- This form of wiring is used in
household circuits.
- Voltmeter - a device for measuring
voltage (or
- potential difference), and must be
wired into the
- circuit in parallel
- Short Circuit - A short circuit
occurs when a
- conducting object such as a
screwdriver lies
- between two circuits. The
electrons take the
- 'shorter' circuit through the
screwdriver.
HOUSEHOLD CIRCUITS
- Fuse - The fuse is a thin wire
with a low melting point near the power source to a house. It heats up
readily and melts to disconnect the circuit to the house when excessive
current flows. The fuse may 'blow' in the event of a power surge to the
house, or due to a faulty electrical appliance in the house. A circuit-breaker
serves a similar purpose.
- Ground/Earth Wire - All households must
have a connection between the household wiring and the earth. This is to
carry away any extra surge of electricity that may occur during lightning
storms or as a result of a faulty appliance.
- Electric Plug - Most electric
plugs have 3 connections - Active or 'Live' (brown), Neutral (blue) and
Earth (green/yellow). However, appliances with plastic exteriors do not always
have the third earth connection.
- DC (Direct Current) - Direct
current is a current in which electrons continually flow in the one
direction. It is produced by batteries.
- AC (Alternating Current) -
Alternating current is a current of electrons in which the direction of
movement of electrons is continually changing. It is the type of current
in household and industrial circuits.
3 WAYS OF GENERATING ELECTRICITY
- Using Chemical Reactions in
Electric Cells - The chemical
energy of the electric cell is converted to electrical energy.
- Using Light in Solar Cells - Solar or photo voltaic cells are
made of elements such as silicon which readily free electrons when exposed
to sunlight energy. The light energy is converted into electrical energy.
- Using Magnets - Moving a magnet through a coil
of wire causes the electrons to flow through the wire. This is called the
electromagnetic effect or induction. Moving the magnet in the opposite
direction causes the current to reverse. To increase the current, one can
increase the strength of the magnet, the number of turns in the coil, or
the speed of movement of the magnet.
OHM'S
LAW
- Voltage or Potential Difference
(volts, V) = Current (amperes, A) × Resistance (ohms, Ω)
V = I × R
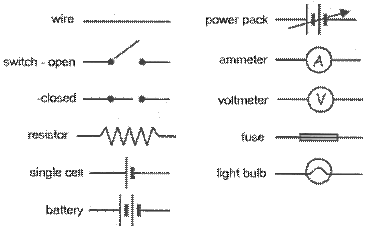
ELECTRICITY SYMBOLS
The best
real-life example of direct current is a battery.
Batteries have
positive (+) and negative (-) terminals. If you take a wire and connect the
positive and negative terminals on a battery, the electrons in
the wires will begin to flow to produce a current. You can prove that the
current is flowing if you connect a small light to the circuit. The light will
begin to glow as the electrons pass through the filaments. Everything that uses batteries runs on DC
power.
Electric wiring in your house is AC power and it is completely different than
DC.

The electricity produced by a generator travels along cables to a transformer, which changes electricity from low voltage to high voltage. Electricity can be moved long distances more efficiently using high voltage. Transmission lines are used to carry the electricity to a substation. Substations have transformers that change the high voltage electricity into lower voltage electricity. From the substation, distribution lines carry the electricity to homes, offices and factories, which require low voltage electricity.
Household electricity is around 240 volts in
some countries and 110v. in others. Such
high voltages may give you deadly shocks,
so appliances are protected by "fuses".
Fuses, contain thin pieces of wire that melt
and cut off current if it is too large. Electricity
is carried to the different parts of the house
by parallel circuits. The parallel circuits
contain 2 wires called the "live and neutral
wires". Some countries use "Earth wire",
which is a safety device that provides a path
to the ground which electric current can
escape
Electrical
Power
- Electrical power is the amount of
electrical energy used by an appliance every second. It is measured in Watts.
- When paying for electricity, we
use the unit kiloWatt-hour (kWh). One kWh is the energy used by a 1000
watt appliance switched on for one hour.
- Example:
Q. A 200 watt TV set is used for 6 hours. How many
kilowatt-hours of electricity were used?
A.
Number of kWh
|
= kilowatts × number of rating hours
|
= (200 W⁄1000)
× 6 h
|
|
|